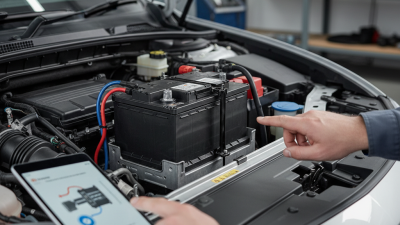
A car battery is a crucial component of any vehicle. It serves as the heart of electrical functions, powering everything from ignition to lights. According to the International Energy Agency, nearly 1.5 billion cars are on the road globally, each relying on reliable battery technology. This highlights the importance of understanding how car batteries work.
Typically, car batteries are lead-acid types due to their cost-effectiveness and efficiency. They provide the necessary voltage to start engines and run electrical systems. However, battery lifespan can vary significantly. Factors like temperature, usage patterns, and maintenance play key roles. Studies reveal that neglecting battery upkeep can lead to premature failures, which many drivers overlook.
Moreover, as electric vehicles rise in popularity, traditional car batteries face challenges. Consumers need to know what affects their battery health. With the right knowledge, they can enhance performance and drive longevity. It’s essential to reflect on this power source and consider its impact on both vehicles and the environment. Understanding car batteries can help in making informed decisions for maintenance and usage.
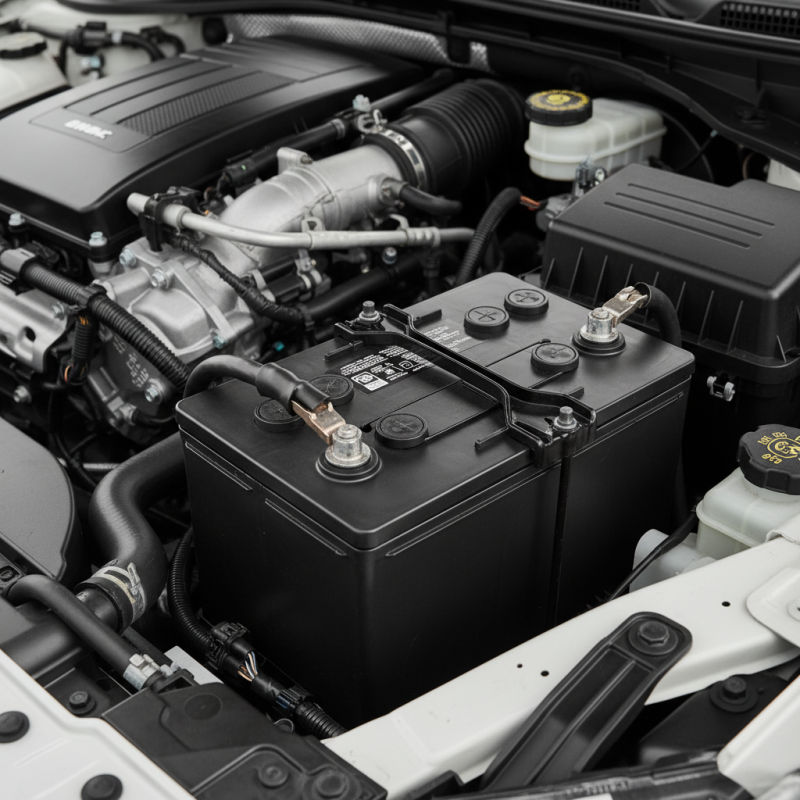

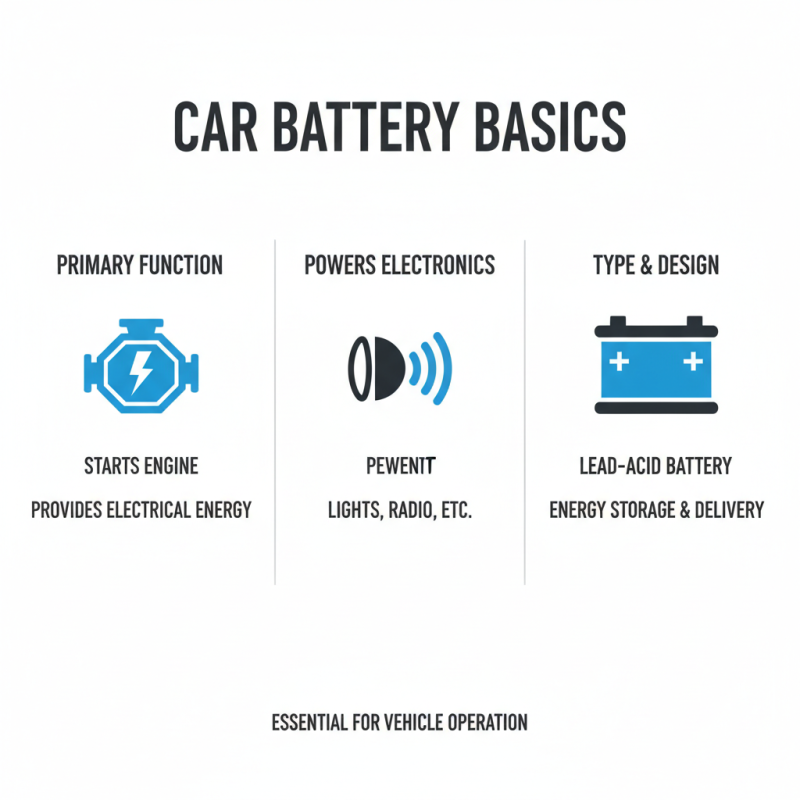
A car battery is a crucial component in any vehicle. It provides the electrical energy needed to start the engine. Additionally, it powers various electronic systems like lights and radio. Generally, car batteries are lead-acid batteries. Their design allows for effective energy storage and delivery.
The purpose of a car battery goes beyond just starting the car. It acts as a stabilizer for the electrical system. When the engine runs, the alternator recharges the battery. This cycle is vital for a vehicle’s optimal performance. However, batteries can deteriorate over time. Factors like temperature and usage influence their lifespan.
Sometimes, car owners overlook battery maintenance. This can lead to unexpected failures. Regular checks on battery terminals and connections are essential. These simple actions can prevent bigger issues. In colder climates, the battery may struggle more. Drivers must be aware of their battery's condition. Ignoring signs of wear can result in inconvenient situations. Keeping a proactive mindset about battery care is necessary.
Car batteries are essential for powering vehicles. They provide the energy necessary to start engines and power electrical components. Two primary types of car batteries dominate the market: lead-acid and lithium-ion. Lead-acid batteries have been around for over 150 years and are known for their robustness. They are typically used in traditional combustion engine vehicles. According to industry data, these batteries account for about 70% of the global automotive battery market. They are relatively inexpensive but have limitations in lifespan and energy density.
Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are gaining traction, especially in electric vehicles. They are lighter and provide higher energy efficiency. Reports indicate that lithium-ion batteries can last up to three times longer than lead-acid batteries. This makes them more appealing despite their higher upfront cost. However, the production and disposal of lithium-ion batteries present environmental challenges. The extraction of lithium can lead to significant ecological damage. Not all recycling methods are efficient, creating more waste. While the performance advantages are clear, the industry faces a balancing act between tech advancement and environmental stewardship.
A car battery is essential for starting vehicles. It provides the electrical energy required to crank the engine. The chemistry behind this operation involves lead-acid reactions. Lead dioxide and sponge lead create a chemical reaction when the battery is charged or discharged.
When the battery discharges, sulfate ions form. This process generates electricity to start the car. During charging, chemical reactions reverse, regenerating active materials. It's a cycle of energy conversion, essential for vehicle operation. The typical car battery has a voltage of 12 volts and a capacity of 45 to 70 amp-hours.
Tip: Regularly check battery levels. Low levels can shorten battery life. Keep terminals clean and corrosion-free to ensure optimal performance.
Battery efficiency decreases over time. Factors like heat and cold impact performance. A study by the Battery Council International indicates batteries last around three to five years. Be proactive about battery maintenance. Small issues today may lead to larger problems tomorrow. Regular testing can save you from unexpected failures on the road.
Car batteries are essential for vehicle functionality. They provide the initial power needed for starting the engine and support electrical systems. Understanding their key specifications can greatly help in choosing the right battery.
Voltage is a critical aspect. Most car batteries operate at 12 volts. However, performance can decrease in extreme temperatures. Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) indicate a battery's ability to start an engine in cold weather. A typical battery may offer around 600 CCA. In colder climates, higher CCA ratings are beneficial. These figures help ensure reliability during harsh winters.
Capacity, measured in amp-hours (Ah), defines how long a battery can supply power. For most cars, a capacity of 50-70 Ah is common. This range supports various electrical systems like lights and infotainment. However, an undersized battery can lead to problems. It might not meet the energy demands of modern vehicles. Proper data analysis is crucial for battery selection. A mismatched battery can affect vehicle performance negatively. This highlights the importance of understanding specifications.
| Specification | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 12V | Standard voltage for most car batteries. |
| Capacity | 50 - 100 Ah | Amp-hour rating indicating battery capacity. |
| Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) | 200 - 800 CCA | Amount of current a battery can provide at 0°F for 30 seconds. |
| Dimensions | Size varies (e.g., 10.2 x 6.9 x 7.5 inches) | Physical size of the battery to fit in the vehicle. |
| Weight | 30 - 50 lbs | Weight affects handling and installation. |
Battery maintenance is crucial for optimal car performance. Regular check-ups can extend battery life significantly. According to the Battery Council International, a battery properly maintained can last up to five years. Yet, many car owners neglect this aspect, reducing battery longevity.
Keeping the battery terminals clean is essential. Corrosion can impede performance. A simple cleaning solution can remove buildup. Checking the electrolyte levels is also critical. Low levels can lead to reduced efficiency. If the battery is sealed, verifying the manufacturer's recommendations is vital.
Extreme temperatures can affect battery health. In cold weather, battery capacity can drop by over 50%. Similarly, excessive heat can increase evaporation rates of electrolyte liquid. Finding a shaded parking spot or using thermal wraps can mitigate these effects. Most importantly, the human element matters. Many overlook small signs of wear, delaying necessary action. Ignoring these can lead to unexpected failures.